Realistic Defocus Blur for Multiplane Computer-Generated Holography¶
People¶
 |
 |
 |
 |
1Koç University, 2The University of Tokyo 3University College London
Resources¶
Bibtex
@misc{kavakli2022realisticdefocus,
doi = {10.48550/ARXIV.2205.07030},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.07030},
author = {Kavaklı, Koray and Itoh, Yuta and Urey, Hakan and Akşit, Kaan},
keywords = {Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV), Graphics (cs.GR), FOS: Computer and information sciences, FOS: Computer and information sciences, I.3.3},
title = {Realistic Defocus Blur for Multiplane Computer-Generated Holography},
publisher = {arXiv},
year = {2022},
copyright = {Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial No Derivatives 4.0 International}
}
Presentation¶
Video¶
Abstract¶
This paper introduces a new multiplane CGH computation method to reconstruct artefact-free high-quality holograms with natural-looking defocus blur. Our method introduces a new targeting scheme and a new loss function. While the targeting scheme accounts for defocused parts of the scene at each depth plane, the new loss function analyzes focused and defocused parts separately in reconstructed images. Our method support phase-only CGH calculations using various iterative (e.g., Gerchberg-Saxton, Gradient Descent) and non-iterative (e.g., Double Phase) CGH techniques. We achieve our best image quality using a modified gradient descent-based optimization recipe where we introduce a constraint inspired by the double phase method. We validate our method experimentally using our proof-of-concept holographic display, comparing various algorithms, including multi-depth scenes with sparse and dense contents.
Results¶
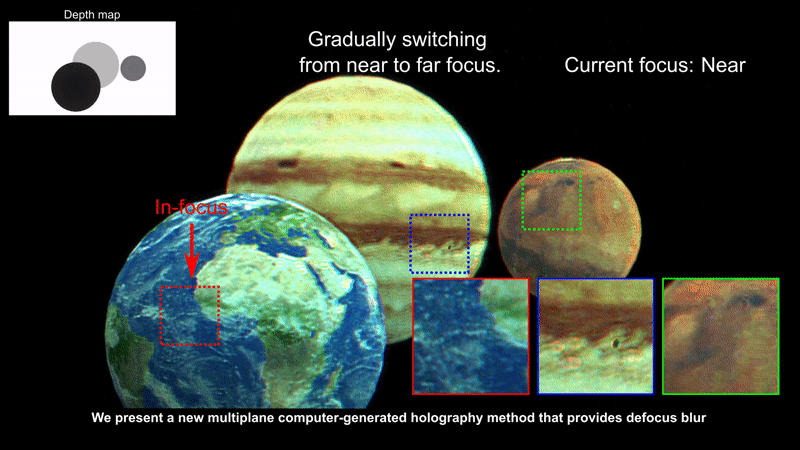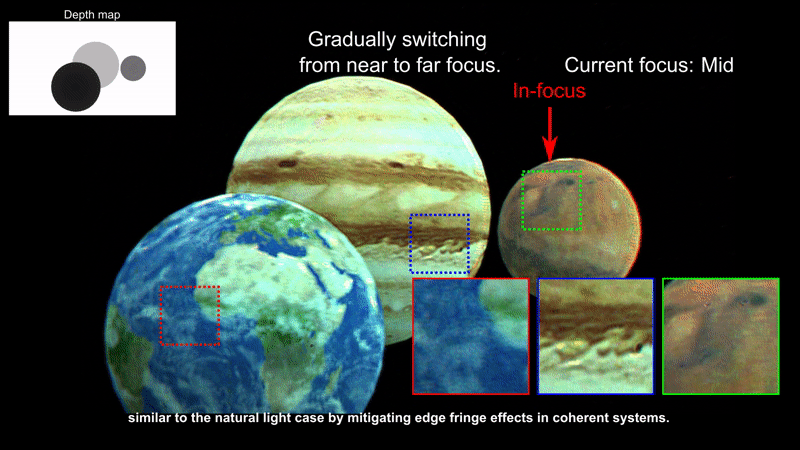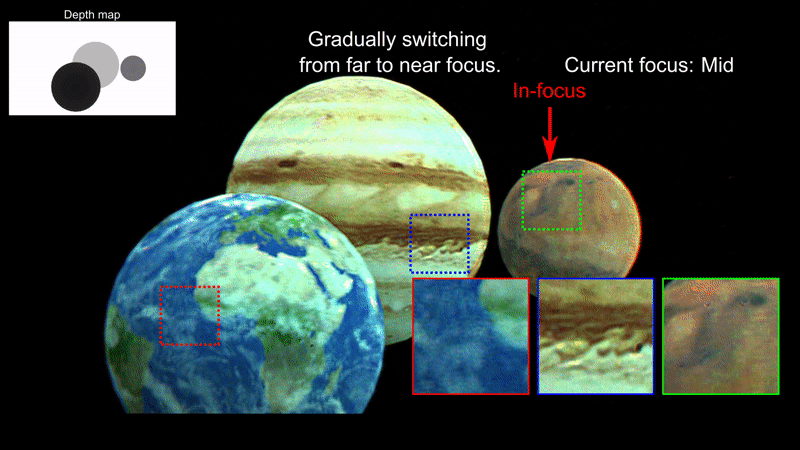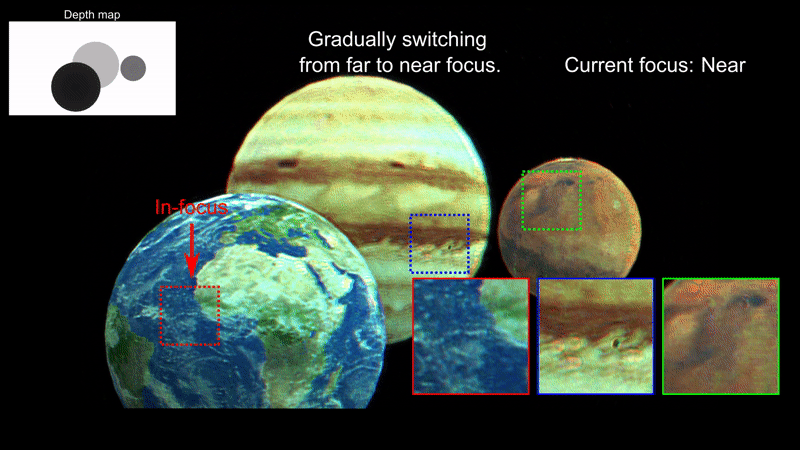
In this work, we demonstrate a new rendering pipeline for multiplane Computer-Generated Holography that can provide near-accurate defocus blur.
Our results suggest that our work can help alliviate unintended artifacts found on existing rendering pipelines for Computer-Generated Holography.
We capture these results using our in-house baked holographic display prototype.
Our technique is suitable for Augmented Reality applications (e.g., near-eye displays, heads-up displays). Here we provide photographs of virtual images generated by our computer-generated holography pipeline overlayed on an actual scene. Note that each image is focused at a different depth level.
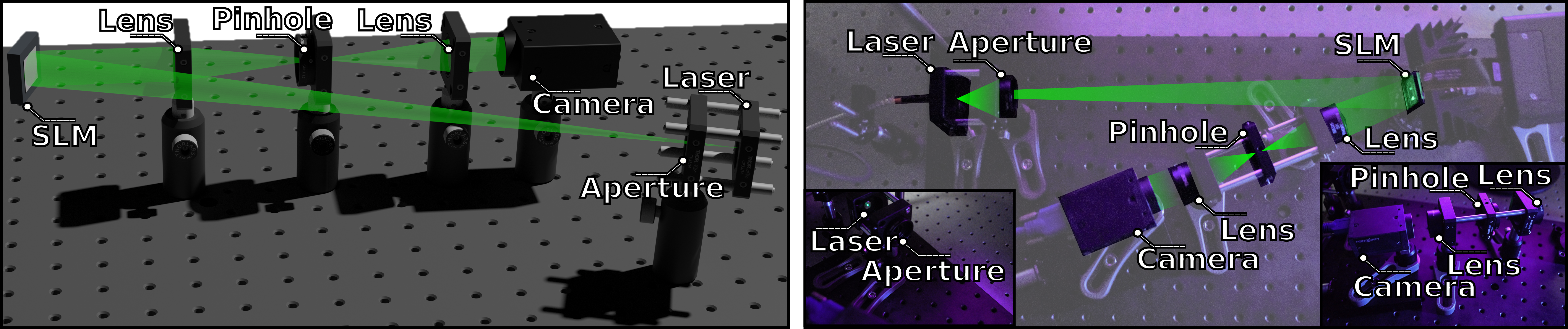
Here we show a photograph of our holographic display prototype with Augmented Reality support.
Relevant works from our group¶
Here are relevant research works from our group:
- Odak
- Metameric Varifocal Holograms
- Learned Holographic Light Transport
- HoloBeam: Paper-Thin Near-Eye Displays
Contact¶
Have any queries, questions, suggestions or comments, contact us via kaanaksit@kaanaksit.com.
Acknowledgements¶
We also thank Erdem Ulusoy and Güneş Aydındoğan for discussions in the early phases of the project; Tim Weyrich and Makoto Yamada for dedicating GPU resources in various experimentation phases; David Walton for his feedback on the manuscript;
Yuta Itoh is supported by the JST FOREST Program Grant Number JPMJPR17J2 and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP20H05958 and JP21K19788.
Hakan Urey is supported by the European Innovation Council's HORIZON-EIC-2021-TRANSITION-CHALLENGES program Grant Number 101057672.
Kaan Akşit is supported by the Royal Society's RGS\R2\212229 - Research Grants 2021 Round 2 in building the hardware prototype.